
Rousseau, Batiste Érard, Stéphane (15 September 2019)."A Beginner's Guide to Working with Astronomical Data".
"Data Mining of the MultiDark Simulation". "The POL-2 Data Reduction Cookbook 1.0" (PDF). Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. "Introducing Nightlight: A New FITS Viewer". "Visualization, Exploration, and Data Analysis of Complex Astrophysical Data".

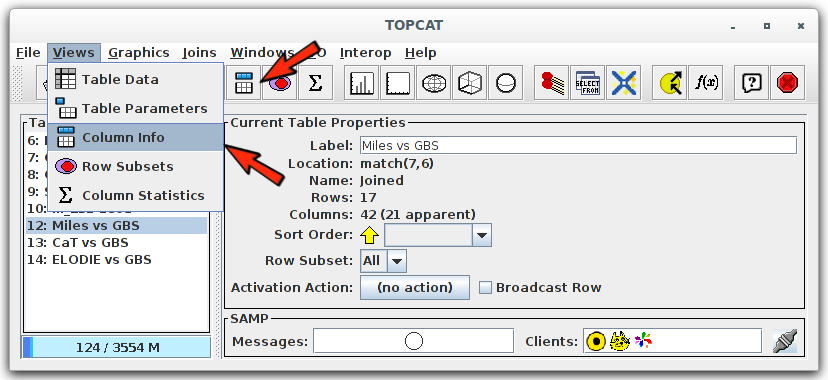
Archived from the original on 15 April 2019. "Virtual Observatory Tools for Astronomers". Archived from the original on 20 October 2018. Archived from the original on 10 January 2019. Archived from the original on 30 January 2018. Applications using TOPCAT include MultiDark, a database for results from cosmological simulations. TOPCAT is used in training for use of virtual observatories. The STILTS application complements TOPCAT with similar capabilities but is considered a steeper learning curve, however STILTS does have the advantage of being able to be scripted. While TOPCAT is unable to visualise catalogues as a set of vectors it does have capabilities to explore correlations in two and three dimensional scatter plots. VisIVO is an alternative tool for working with virtual observatories. Muna, in his 2016 paper "Introducing Nightlight: A New FITS Viewer", observes that SAOImage DS9, TOPCAT and Fv are the most common tools used to view FITS files. It is suitable for use as a graphical viewer and data editor of tabular data from FITS and other sources. Written in Java, TOPCAT can be used both standalone and within a web browser. Initially funded from the Starlink Project it has been funded by various other projects since.
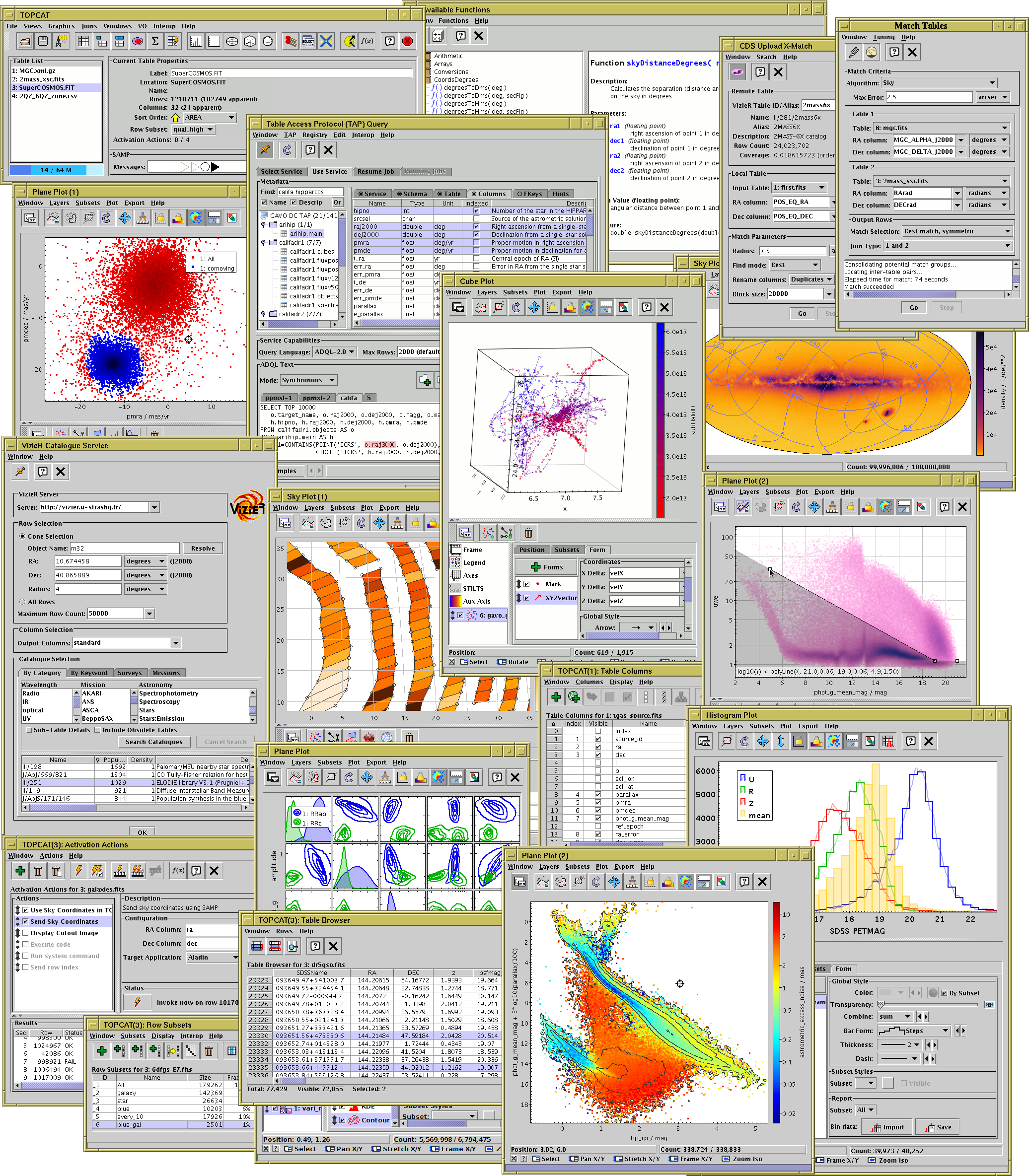
Taylor acknowledges inspiration for some features from Mirage from Bell Labs and VOPlot from VO-India. The project was initially developed by Mark Taylor, an astrophysicist from the University of Bristol in 2003.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
